Emerging Trends in Supply Chain Management 2025: Cloud ERP, AI & More
Section
Table of Contents
- Microsoft’s Solutions for Supply Chain Management
- Trend 1: Advanced Data Integration and Cloud Platforms
- Trend 2: Role of Internet of Things (IoT) and Sensor Technologies
- Trend 3: Predictive Analytics and Machine Learning Applications
- Trend 4: Digital Twin and Simulation Technology
- Integration with ERP and Enterprise Systems
- Dashboard Integration and Visualization: A Strategic Tool for Decision-Makers
- Business Benefits and Operations Use Case
- Conclusion
- FAQs ( Frequently Asked Questions)
- AI, Cloud ERP, and IoT are going to further transform supply chain management by delivering efficiency upgrades, reducing costs, and enabling real-time decision-making.
- Predictive analytics and automation help businesses mitigate risks, optimize logistics, and enhance supplier collaboration, ensuring smoother operations and better customer satisfaction.
- Scalable, cloud-based solutions allow companies to adapt to market changes and expand efficiently, using digital tools to improve inventory management, sustainability, and overall supply chain resilience.
In 2025, supply chain management faces significant technical challenges that require sophisticated data processing and real-time operational analysis. Modern supply chains must manage vast quantities of data generated by global operations and IoT devices while maintaining secure, high-speed connections across distributed networks. Microsoft has made a notable commitment to offering cloud‐based, data‐intensive solutions designed for worldwide supply chain operations.
Microsoft’s Solutions for Supply Chain Management
Microsoft offers a set of cloud-based applications that consolidate supply chain operations into a unified framework. Microsoft Dynamics 365 Supply Chain Management centralizes production, inventory, and distribution processes, providing a single interface for handling operational data. The Microsoft Cloud for Supply Chain processes real-time information from multiple sources, facilitating immediate data assessment for critical decision-making. This portfolio includes Azure Digital Twins, which create digital models of physical assets for simulation and analysis, and Azure IoT, which gathers sensor data to monitor equipment and processes with precision.
Built on Microsoft Azure, these solutions rely on a cloud platform designed for high availability and scalable data processing. The architecture accommodates the significant volume of data produced by global supply chain operations. It integrates advanced analytics and machine learning models that process historical and streaming data, resulting in insights that inform operational adjustments. The technical design supports event-driven architectures and message broker systems to manage data flows with minimal delay, while adhering to stringent security protocols as detailed in Microsoft’s technical documentation.
This technical framework delivers complete visibility across supply chain activities. Enterprises can monitor processes in real time, identify anomalies in production and logistics, and modify operations based on current conditions. By connecting various systems through standardized APIs, Microsoft’s portfolio offers integrated operational control across manufacturing, warehousing, and transportation. The combined functionality of these solutions facilitates detailed analysis and precise execution of supply chain processes—a critical capability for executive decision-making in large organizations.
Recalibrate Supply Chain Operations. Move to Microsoft Dynamics 365 ERP.
Trend 1: Advanced Data Integration and Cloud Platforms
Microsoft Azure serves as the backbone for data collection and processing in supply chain operations. It plays a crucial role in gathering data from diverse sources such as sensors, transactional systems, and external applications. Key components of this technical framework include:
Cloud Infrastructure and Data Storage
- Microsoft Azure supports the creation of centralized data repositories.
- Data lakes are employed to store raw, unstructured data from multiple endpoints.
- Centralized storage facilitates access to both historical and real-time operational data, following strict security protocols and data integrity standards as outlined in Microsoft’s technical documentation.
Real-Time Data Processing
- Azure’s architecture allows for immediate data ingestion from global operations.
- The platform uses event-driven architectures to process data as it arrives.
- Message brokers like Azure Event Hubs and Azure Service Bus manage high-volume data streams, which are critical for supplying data feeds from various supply chain systems.
- This design minimizes delays in data handling and supports real-time monitoring and reporting.
Enterprise Data Management
- The cloud environment supports high-speed transaction processing with low latency, relying on distributed computing and in-memory processing techniques.
- Microsoft provides guidelines on integrating supply chain data with existing enterprise resource systems through standardized APIs and connectors.
- This integration consolidates data from disparate systems, creating a unified view for rapid reporting and decision-making.
- Detailed technical guidance is available in Microsoft’s official documentation to support seamless connectivity between supply chain platforms and enterprise resource planning systems.
Trend 2: Role of Internet of Things (IoT) and Sensor Technologies
Microsoft employs IoT and sensor technology to gather, process, and analyze operational data within supply chain systems. The technical implementation is divided into the following components:
Azure IoT Hub and Device Connectivity
- Azure IoT Hub serves as a centralized service to manage device connections from various endpoints.
- It supports protocols such as MQTT, AMQP, and HTTPS for secure data transfer.
- Device authentication relies on secure tokens and certificates, while data encryption is applied during storage and transit.
Sensor Deployment and Data Acquisition
- Sensors are installed to monitor variables like temperature, humidity, vibration, and other critical parameters for sensitive items.
- Calibration processes are in place to maintain sensor accuracy and reliability.
- Edge computing devices perform preliminary data processing close to the sensor source, reducing latency and the amount of raw data sent to the cloud.
- Standard data acquisition methods record environmental parameters consistently across multiple operational zones.
Data Aggregation and Signal Processing
- Collected sensor data is aggregated via Azure IoT Hub into centralized storage solutions such as data lakes, where strict security measures protect the data.
- Processing services, for example Azure Stream Analytics, examine data streams in real time to identify anomalies or trends.
- Processed data is presented on real-time dashboards, enabling operators to view snapshots of current conditions through dynamic dashboards.
- Alert systems are configured to trigger notifications when sensor readings exceed predefined thresholds, supporting rapid corrective actions.
Trend 3: Predictive Analytics and Machine Learning Applications
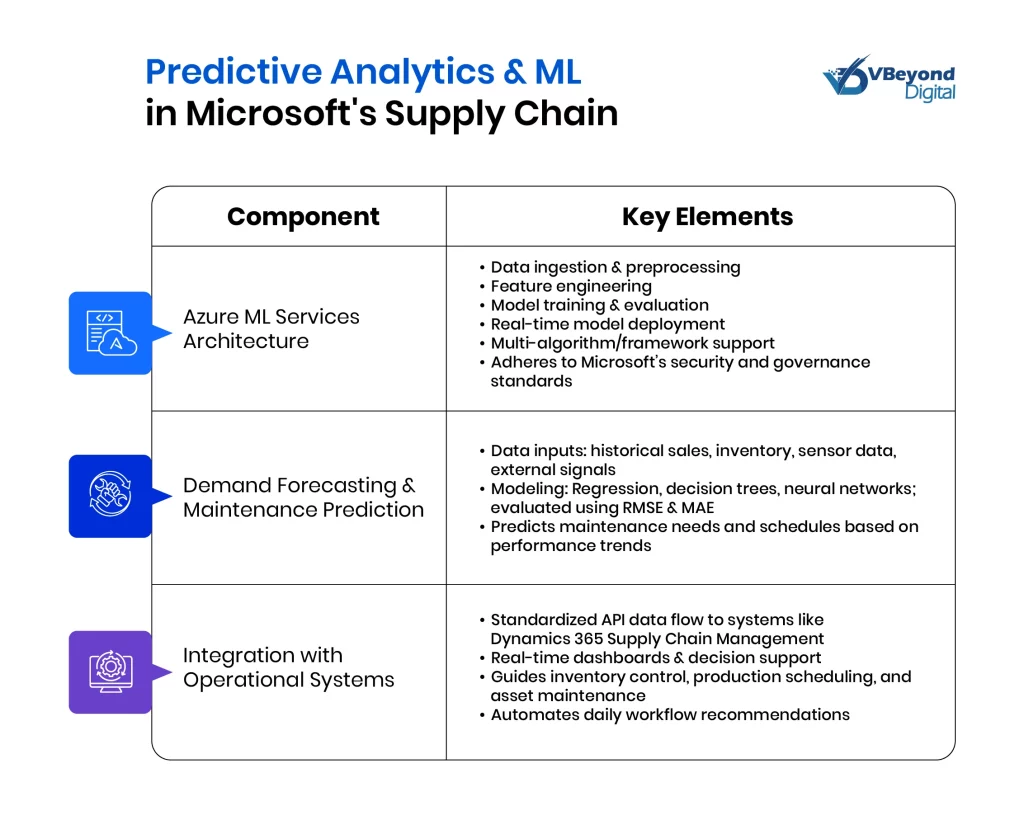
Microsoft integrates predictive analytics and machine learning into its supply chain systems through Azure Machine Learning Services. This approach is built to process both historical and real-time data to support informed decision-making. Key aspects include:
Azure Machine Learning Services Architecture
- Provides a cloud-based platform to build, train, and validate predictive models.
- Involves stages such as:
- Data ingestion and preprocessing
- Feature engineering
- Model training and evaluation
- Deployment of models for real-time use
- Supports a range of algorithms and frameworks while adhering to Microsoft’s security and governance standards.
Demand Forecasting and Maintenance Prediction
- Data Inputs:
- Uses historical sales, inventory, and sensor data.
- Incorporates external signals where available.
- Modeling Techniques:
- Applies statistical models and machine learning methods (e.g., regression, decision trees, neural networks).
- Involves careful selection of features and continuous evaluation using metrics such as RMSE and MAE.
- Maintenance Prediction:
- Processes equipment sensor data to predict potential maintenance needs before failures occur.
- Supports scheduling of maintenance based on predicted performance trends.
Integration with Operational Systems
- Data Flow
- Model outputs are transmitted via standardized APIs into systems like Dynamics 365 Supply Chain Management.
- Real-time dashboards and decision support systems receive these insights for actionable outcomes.
- Operational Impact:
- Predictive outputs guide inventory control, production scheduling, and asset maintenance decisions.
- Automated recommendations are incorporated into daily workflows, providing timely inputs for process adjustments.
Trend 4: Digital Twin and Simulation Technology
Microsoft’s Azure Digital Twins is a cloud service that models physical supply chain components in a digital environment. It provides a virtual representation of physical assets such as production facilities, warehouses, and transportation networks. This digital model uses a graph-based data structure to depict devices, sensors, and their relationships, creating an accurate map of the physical system.
Key components include:
Digital Twin Modeling
- Graph-Based Representation:
- Uses data models that map connections among physical assets and processes.
- Represents relationships between inventory, machinery, and facility layouts.
- Real-Time Data Synchronization:
- Integrates data from IoT devices and other operational systems.
- Maintains an up-to-date digital view of physical operations.
Simulation and Scenario Analysis
- Simulation Tools:
- Runs simulations to emulate operational conditions such as changes in production schedules or supply fluctuations.
- Assesses the impact of simulated events (e.g., equipment downtime or sudden demand variations) on supply chain performance.
- Scenario Analysis:
- Enables testing of different operational scenarios in a virtual environment.
- Assists in decision-making by providing quantitative data on potential disruptions and recovery plans.
Practical Implementations and Integration
- Case Examples:
- Digital twins are applied to monitor inventory flow in warehouses, forecast potential disruptions, and assess network performance.
- They support planning decisions by simulating various operating conditions and measuring the outcome.
- System Integration:
- Interfaces with Dynamics 365 Supply Chain Management and Azure IoT to maintain data consistency.
- Data from digital twins is visualized through Microsoft Power BI and Azure dashboards, allowing executives to review performance metrics quickly.
- Data Synchronization and Visualization:
- Synchronizes real-time sensor data with digital models.
- Uses reporting tools to present key performance indicators and simulation results.
Integration with ERP and Enterprise Systems
Microsoft Dynamics 365 Supply Chain Management integrates with third-party ERP systems and other enterprise applications through standardized interfaces and well-documented APIs. Key technical components include:
Interoperability Standards and APIs
- Provides RESTful APIs that follow OpenAPI specifications for consistent data exchange.
- Pre-built connectors in Microsoft Power Platform enable direct communication with Dynamics 365 Finance, Business Central, and other Microsoft applications.
- Middleware and web services facilitate real-time data synchronization and support standard data transformation protocols.
Unified Data Models and Workflows
- Supports a single data model that consolidates operational information across supply chain and business applications.
- Middleware components handle data transformation and error-handling to manage discrepancies during synchronization.
- Standard workflows allow consistent operational reporting and reduce manual intervention.
Operational Case Studies
- Microsoft documentation presents examples where integrated data from Dynamics 365 Supply Chain Management and ERP systems delivers real-time reporting via Power BI dashboards.
- These cases illustrate the benefits of using RESTful APIs and standardized connectors to provide a unified view of financial, inventory, and logistics information.
Dashboard Integration and Visualization: A Strategic Tool for Decision-Makers
For enterprise leaders and decision-makers, the ability to instantly interpret operational performance in a single, clear interface enhances agility in decision-making. Instead of waiting for monthly reports or piecing together data from different departments, they can rely on dynamic dashboards to track efficiency, costs, and supply chain risks in real time. This capability enables organizations to pivot faster in response to market shifts, supplier disruptions, or changes in customer demand.
Powered by Microsoft Power BI and integrated with Azure analytics services, enterprises can build custom platforms that can convert vast data streams into interactive, customizable views that highlight key performance indicators (KPIs) and operational trends. An integrated solution can deliver:
- Real-Time Data Feeds: Dashboards pull live data from multiple sources—including IoT sensors, ERP systems, and logistics platforms—to provide an always-updated view of supply chain performance.
- Customizable Views: Executives can tailor dashboards to focus on the metrics that matter most—whether it is supplier performance, inventory turnover, transportation costs, or demand fluctuations.
- Drill-Down Capabilities: Leaders can move from a high-level overview down to specific operational details with a single click, enabling deeper analysis of performance trends and anomalies.
- Predictive Alerts & Anomaly Detection: AI-driven insights flag potential disruptions before they happen, allowing leaders to make proactive adjustments rather than react to issues as they arise.
- Multi-Device Accessibility: Whether in the boardroom or on the move, executives can access dashboards via desktop, tablet, or mobile devices, ensuring that critical information is always at their fingertips.
- Integration with ERP & Other Business Systems: Data seamlessly flows from Microsoft Dynamics 365, Azure Digital Twins, and other enterprise tools, creating a unified view across procurement, manufacturing, distribution, and customer demand.
Business Benefits and Operations Use Cases
Logistics & Distribution Optimization
Retailers with multi-channel operations and B2C/D2C online sellers can reduce transportation costs and improve delivery speed with AI-driven inventory optimization. Improved logistics efficiency also helps reduce storage costs by preventing unnecessary stock buildup and ensuring products are available across sales channels. Integrations enabling real-time tracking enables adjustments based on weather, traffic, and supply chain disruptions, ensuring on-time shipments. preventing stock imbalances. This enhances customer satisfaction by reducing stockouts and delivery delays while improving cash flow management through optimized inventory allocation.
Manufacturing & Inventory Management
Manufacturers can prevent production delays by using IoT sensors to monitor machine health. Predictive maintenance reduces downtime by alerting teams before failures occur, while automated inventory tracking ensures raw materials are available when needed, preventing shortages, and reducing waste. These automated workflows streamline operations, lowering operational expenses and improving productivity.
Supplier & Risk Management
Enterprises with high-volume and high-value shipments like automotives, heavy electronics, pharmaceuticals, and more, can minimize supply chain disruptions by using AI to evaluate variables such as supplier reliability and external risks. Predictive analytics help identify potential delays due to geopolitical shifts or material shortages, allow businesses to proactively adjust sourcing strategies and maintain steady production. Improved supplier collaboration through centralized platforms reduces miscommunication and enhances procurement efficiency.
End-to-End Business Orchestration
- Sales & Revenue Ops: Syncing Dynamics 365 Sales and Business Central enables real-time pipeline tracking, automated quote-to-cash, and AI-driven upsell opportunities.
- Distribution Efficiency: Third-party ERP integration gives real-time stock updates and insights on distribution activities to help plug gaps quickly.
- E-Commerce & Retail Expansion: Connecting Dynamics 365 Commerce and online platforms centralizes orders, unifies pricing, and personalizes customer experiences.
- Financial & Risk Management: Linking Dynamics 365 Finance and Business Central automates reporting, tax compliance, cash flow tracking, and AI-powered supplier risk assessment.
Conclusion
Microsoft’s supply chain solutions combine essential technical components such as cloud-based data consolidation using Azure, IoT connectivity through Azure IoT Hub with digital twin simulation, and predictive analytics via Azure Machine Learning Services to manage operational data effectively. Robust security protocols—including encryption, multi-factor authentication, continuous monitoring, and detailed audit trails—safeguard information and support regulatory compliance. Integration with ERP systems and other enterprise applications results in improved data management, increased operational visibility, and more precise decision-making, all critical for operational planning and strategic investments.
FAQs
Microsoft Dynamics 365 Supply Chain Management is a cloud-based solution that integrates production, inventory, and logistics into a single platform. It enables real-time monitoring, automates workflows, and improves decision-making with AI-driven insights.
Microsoft Cloud for Supply Chain consolidates data from multiple sources, providing real-time analytics and predictive insights. It connects systems through APIs, ensuring smooth information flow between manufacturing, warehousing, and transportation operations.
IoT and sensor technologies gather key operational data such as temperature, humidity, and equipment status. This data is processed immediately, offering a clear view of supply chain conditions. Local processing minimizes delay in communication and helps managers quickly address issues that may affect production or logistics.
Azure IoT collects sensor data from equipment, vehicles, and warehouses to monitor conditions such as temperature, humidity, and machine performance. This data is processed in real time to detect issues early and prevent disruptions.
Predictive analytics uses historical data and AI models to forecast demand, anticipate maintenance needs, and identify potential delays. Microsoft’s Azure Machine Learning Services powers these predictions, helping businesses make proactive adjustments.
Digital Twins create virtual models of physical supply chain components, allowing businesses to run simulations, test scenarios, and assess risks. Microsoft Azure Digital Twins helps organizations refine strategies before making operational changes.
Yes, Microsoft Dynamics 365 Supply Chain Management and related tools integrate with third-party ERP systems through APIs and pre-built connectors. This ensures smooth data exchange and maintains consistency across enterprise applications.
Azure processes high-volume data using event-driven architectures, data lakes, and real-time analytics. It supports secure storage and rapid access, enabling businesses to track operations across global supply networks efficiently.
Microsoft employs multi-layered security, including encryption, multi-factor authentication, continuous monitoring, and compliance with industry regulations. These measures protect sensitive supply chain data from unauthorized access.
Organizations can begin by assessing their supply chain needs and consulting with a Microsoft-certified partner. Microsoft offers migration tools, implementation support, and documentation to assist with deployment.




